Intermittent Fasting (IF) has revolutionized the concept of dieting and health maintenance, turning the spotlight not just on what we eat but when we eat. This Guide to Intermittent Fasting unpacks the science behind intermittent fasting, explores its myriad health benefits, introduces the most popular fasting methods, and offers actionable tips to integrate this healthful practice into your life.
Why Consider Intermittent Fasting?
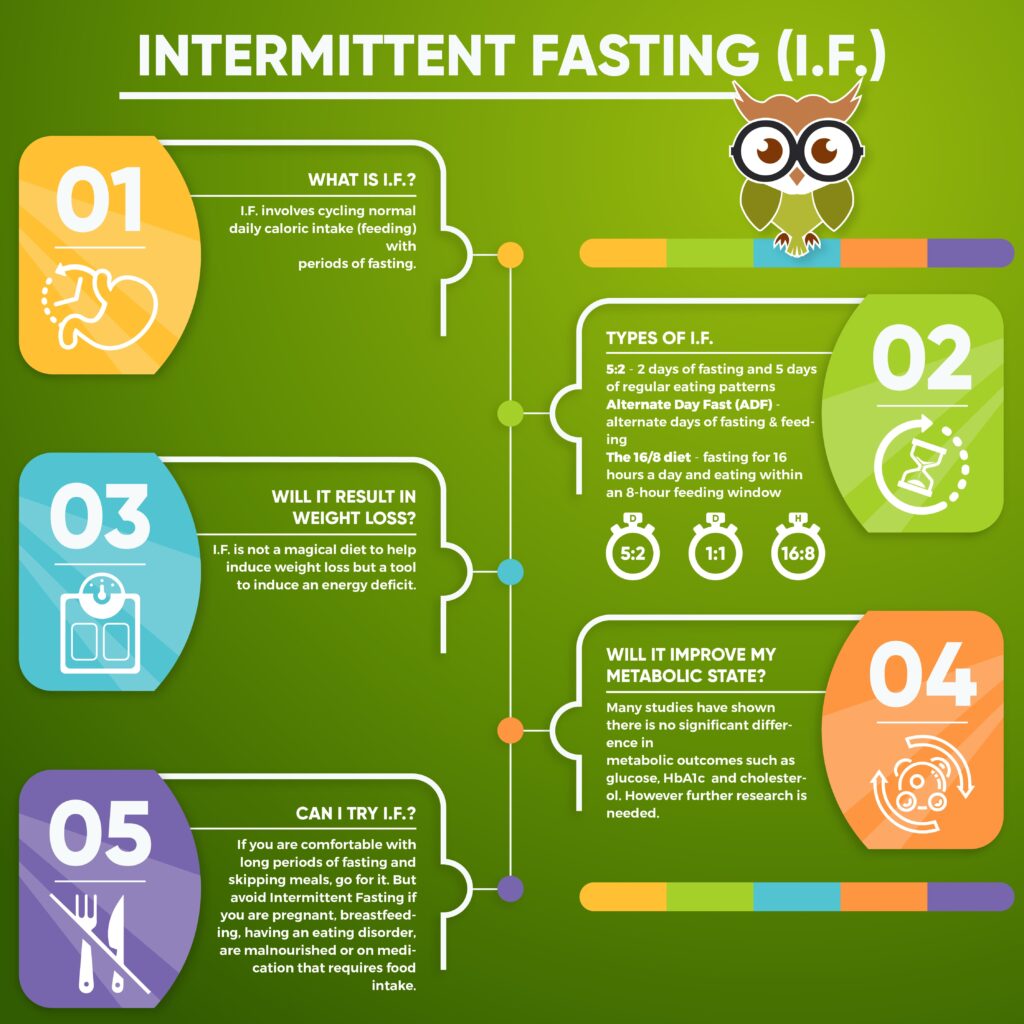
Guide to Intermittent Fasting – Intermittent fasting isn’t merely a diet trend; it’s a sustainable lifestyle change backed by growing scientific evidence. It offers an alternative to the daily caloric restriction model, proposing significant periods of fasting interspersed with eating windows. This approach has been linked to numerous health benefits, including weight loss, improved metabolic health, and even a potential increase in lifespan.
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
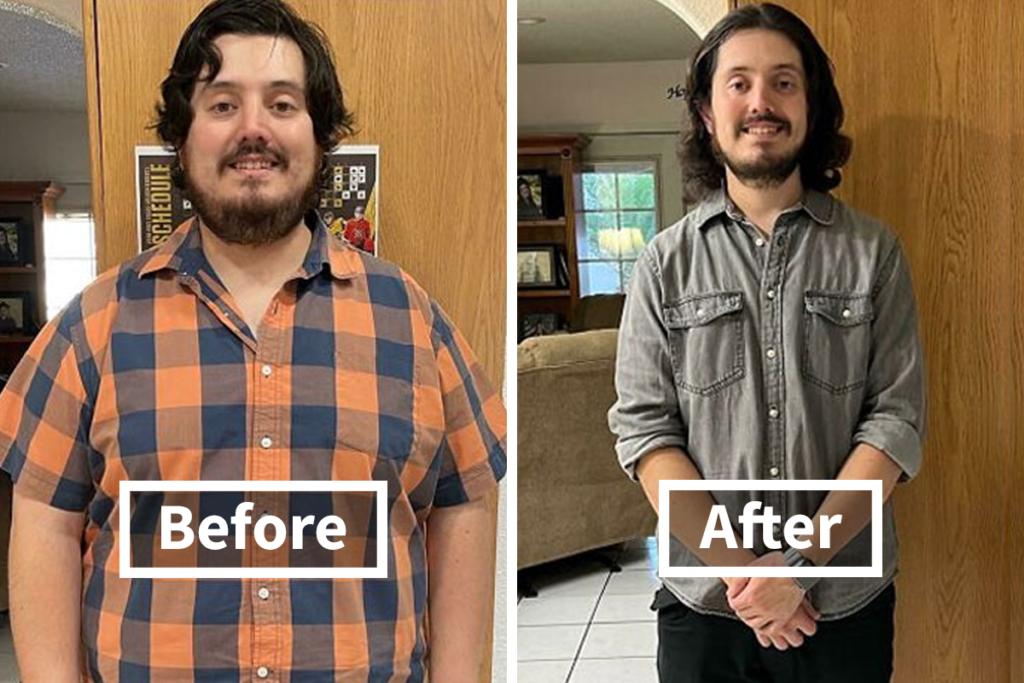

Weight Loss and Body Composition
One of the most sought-after benefits of IF is weight loss and fat loss. By limiting the eating window, many find it naturally reduces overall calorie intake. Moreover, fasting periods initiate hormonal and metabolic changes, enhancing fat burning and improving metabolic health.
Enhanced Brain Function
Intermittent fasting can have profound benefits on brain health, including improved memory, cognition, and resistance to neurodegenerative diseases. Fasting stimulates the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports brain health and cognitive function.
Heart Health
Adopting IF can lead to improvements in various cardiovascular risk factors, including blood pressure, cholesterol levels, triglycerides, and inflammatory markers.
Cellular Repair and Longevity
Fasting triggers autophagy, the body’s way of cleaning out damaged cells, which can lead to a reduced risk of several diseases and has been associated with longevity.
Insulin Sensitivity and Diabetes Risk
Intermittent fasting can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels, which may lower the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Understanding Intermittent Fasting Methods
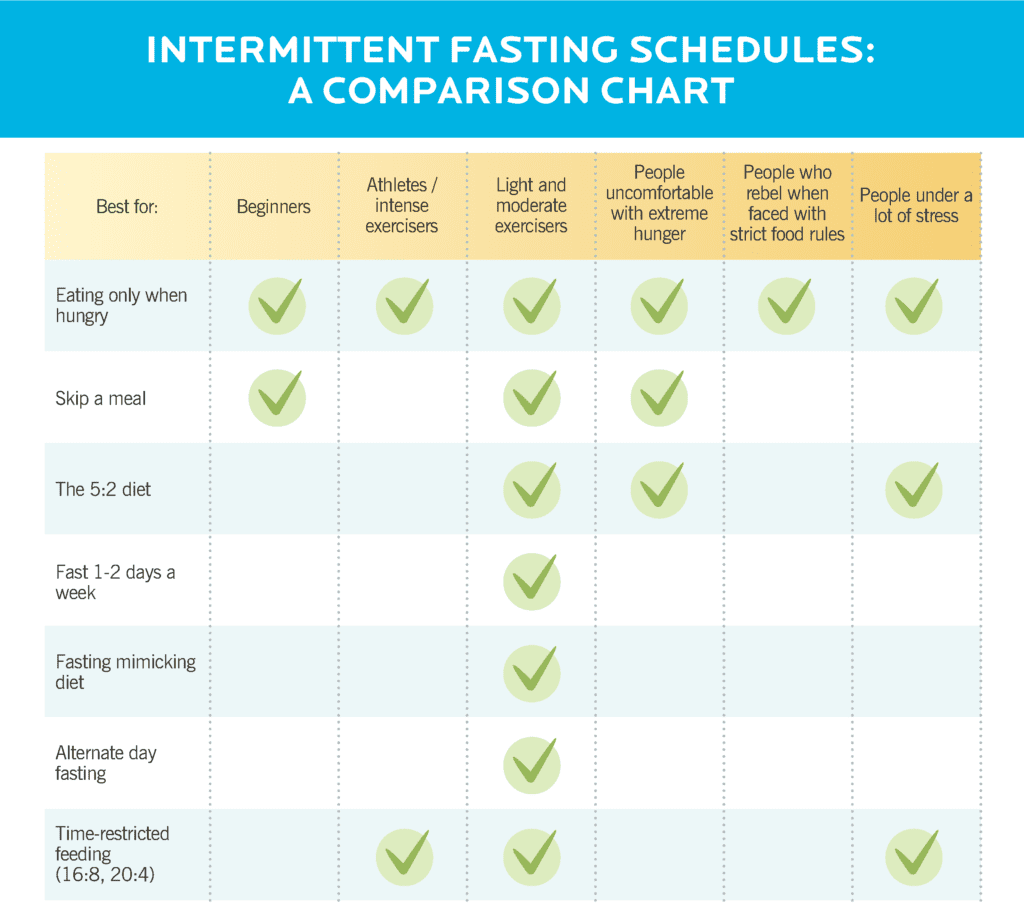
The 16/8 Method: Also known as the Leangains protocol, it involves fasting for 16 hours each day and eating during an 8-hour window.
The 5:2 Diet: This method involves eating normally five days a week and restricting calories to about 500–600 for two days of the week.
Eat-Stop-Eat: This involves a 24-hour fast once or twice a week.
Alternate-Day Fasting: Involves fasting every other day, either by not eating anything or by significantly reducing calorie intake during fasting days.
The Warrior Diet: Eating small amounts of raw fruits and vegetables during the day and one large meal at night.
Spontaneous Meal Skipping: Skipping meals when convenient, without the need to follow a structured fasting plan.
How to Start Intermittent Fasting Safely
Begin Gradually: Start with shorter fasting periods and gradually increase the duration as your body adjusts.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water and calorie-free beverages throughout the day to stay hydrated.
Eat Nutritious Foods: Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods during your eating windows to maximize health benefits.
Monitor Your Body’s Response: Pay attention to how your body responds to intermittent fasting and adjust your approach as needed.
Tips for Success with Intermittent Fasting
Plan Your Meals: Planning helps you make the most of your eating windows with nutritious foods that support your health and fasting goals.
Incorporate Healthy Fats and Proteins: These nutrients can help keep you feeling full and satisfied during your fasting periods.
Exercise Moderately: While heavy workouts might be challenging during fasting periods, moderate exercise can complement your IF plan.
Expect an Adjustment Period: It’s normal to experience hunger and fatigue as your body adapts to your new eating schedule.
Consider Using a Fasting App: Many find tracking their fasting and eating windows with an app helpful for staying on track.
Potential Challenges and How to Overcome Them – Guide to Intermittent Fasting
Hunger: Common in the beginning, but it usually decreases as your body adapts. Drinking water or tea can help manage hunger pangs.
Social Eating: Plan your fasting periods around your social events when possible. Being flexible with your fasting schedule can make IF more sustainable.
Overeating: Avoid the temptation to overeat during eating windows by focusing on nutrient-dense foods that provide lasting satiety.
Related Products to Enhance Your Intermittent Fasting Journey
Fasting Apps: Tools like Zero or MyFitnessPal can help track your fasting windows and nutritional intake.
Water Bottles with Time Markers: Encourage regular hydration throughout the day.
Healthy Snack Subscriptions: Services that deliver healthy snacks can make it easier to find nutritious options during your eating windows.
Books and Guides: Comprehensive resources on intermittent fasting can provide deeper insights and motivation.
Conclusion
In this Guide to Intermittent Fasting we can see that IF offers a flexible approach to eating that can lead to numerous health benefits. By understanding the various methods, starting gradually, and listening to your body, you can find a fasting rhythm that enhances your health and fits your lifestyle. Remember, the key to successful intermittent fasting is consistency, patience, and a focus on overall nutrition.



